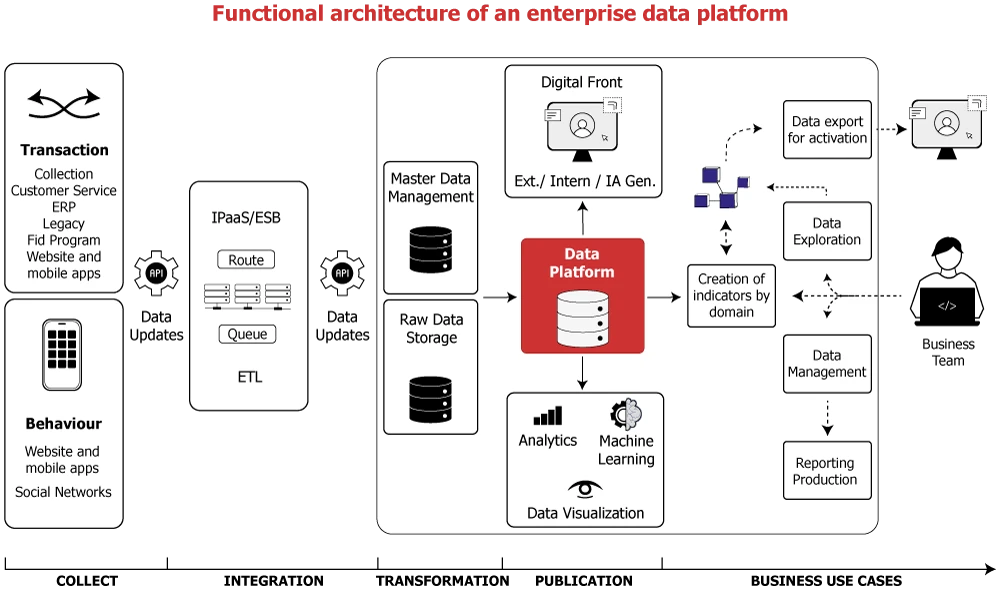
Data is often siloed within business applications. The Data Platform allows for the valorization of this data by connecting it across different domains. Data truly transforms into “assets,” making the company “data-centric.”
Platformization, based on a centralized architecture, is built around workspaces and enables moving beyond the logic of business “use cases,” empowering everyone to achieve their goals. Data becomes a reliable and available “product.”
The platform ensures data mastery:
- Data reliability
- 360° data visibility
- Data accessibility and sharing
But also governs it:
- Monitoring and observability of data
- Data traceability and security
- Compliance with regulatory requirements: GDPR, etc.